FinUgRevita
Project

Research Focus:
The FinUgRevita Project develops computational tools to aid in language learning and supporting endangered languages.The main goals of our tools:
-
Stimulate active linguistic competence: rather than
passive absorption of linguistic knowledge, the learners exercise
their ability to construct correct word forms based on the given
context. The context is provided by a story. Stories can be
chosen by the learnerfrom
different genres: fiction, journalism, poetry, etc.
Provide an unlimited variety of learning material:
the stories can come from our on-line library of pre-selected
texts, or from any other source that the user specifies. The goal
is that the user learns from stories that s/he finds
interesting.
Model the state of user competence and the user's
progress toward complete fluency. The principal challenge for the
computational learning environment is to
present questions to the student that are at the appropriate
level of difficulty -- the questions are not
too easy and not too difficult.
-
If they are too easy, the user will become bored
and will quit learning.
If they are too difficult, the user will
become discouraged and will quit learning.
The Project is jointly supported by:
-
FinUgRevita Project of the Academy of Finland (Project number: AKA 267097)
Hungarian
National Research Fund: OTKA (Project number: OTKA FNN107883)
People:
-
Vuokko Hangaslahti
University of Helsinki
Master's student (2014-) Javad Nouri
University of Helsinki
MSc student Kirill Reshetnikov,
Russian Academy of Sciences,
Institute of Linguistics, Moscow Marjo Sutinen
University of Helsinki
Master's student (2014-) Roman Yangarber
University of Helsinki
Project Lead
Collaboration:
-
The Hungarian partner team:
University of Szeged, Hungary.
Project Lead: Prof Anna Fenyvesi. Elävä Kieli -- Живой Язык -- Living Language:
Helsinki, Finland.
Organization for revitalization and
strengthening of minor Finno-Ugric Languages Tibidiscis, Oy:
Helsinki company specializing in computer assisted language learning Giellatekno: Platform for language technology tools,
focusing on Saami and other Uralic languages;
University of Tromsø, Norway. The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), Institute of Linguistics. The StarLing Project, a collection of large etymological databases for many language families of the world. KOTUS: analysis and enhancement of data in the Finnish etymological dictionary "Suomen Sanojen Alkuperä". (This database is proprietary, and will be released for public access soon. Please contact us or KOTUS to request permission to access.)
Resources:
-
Project
Wiki
(Internal use, registration needed) Wiki: Computational historical linguistics
and modeling population history Web-based etymological database,
Suomen Sanojen Alkuperä:
Finnish Etymological Dictionary
(To be published on the Web by KOTUS;
please contact us to request access)
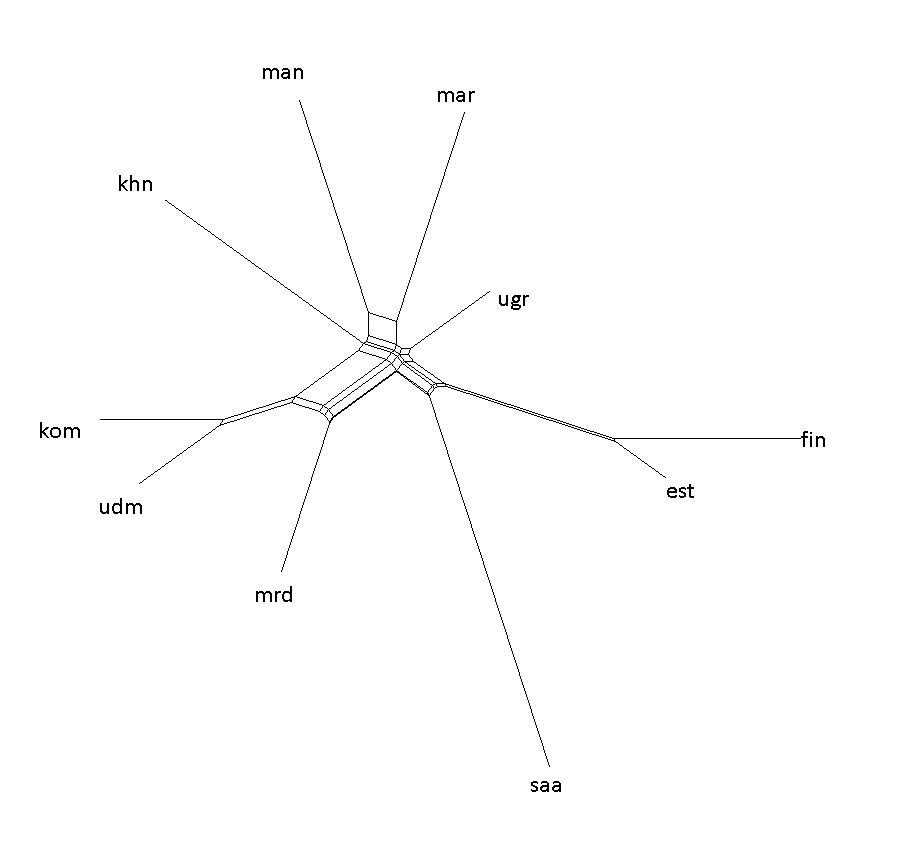
Project Publications:
Conference and Journal Papers, Book Chapters, Theses
Measuring Language Closeness by Modeling Regularity (pdf)Javad Nouri, Roman Yangarber In Proceedings of the EMNLP 2014 Workshop on Language Technology for Closely Related Languages and Language Variants
(2014) Doha, Qatar MDL-based Models for Transliteration Generation (pdf)
Javad Nouri, Lidia Pivovarova, Roman Yangarber SLSP 2013: International Conference on Statistical Language and Speech Processing
Springer Verlag, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence (LNAI) Volume 7978, (2013) Tarragona, Spain Information-theoretic modeling of etymological sound change (abstract)
Hannes Wettig, Javad Nouri, Kirill Reshetnikov and Roman Yangarber Invited chapter in Approaches to measuring linguistic differences (Lars Borin, Anju Saxena, eds.) Trends in Linguistics Series, Volume 265.
(2013) Mouton de Gruyter Probabilistic, Information-Theoretic Models for Etymological Alignment (pdf)
Ph.D. Thesis: Hannes Wettig (2013) University of Helsinki, Department of Computer Science Information-theoretic Methods for Analysis and Inference in Etymology (pdf)
Hannes Wettig, Javad Nouri, Kirill Reshetnikov and Roman Yangarber In Proceedings of WITMSE-2012: the Fifth Workshop on Information-theoretic Methods in Science and Engineering (Steven de Rooij, Wojciech Kotłowski, Jorma Rissanen, Petri Myllymäki, Teemu Roos & Kenji Yamanishi, eds.)
(2012) Amsterdam, the Netherlands Minimum Description Length Modeling of Etymological Data (pdf)
Master's Thesis: Suvi Hiltunen (2012) University of Helsinki, Department of Computer Science Using Context and Phonetic Features in Models of Etymological Sound Change (pdf)
Hannes Wettig, Kirill Reshetnikov and Roman Yangarber. In Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (EACL) Workshop on Visualization of Linguistic Patterns and Uncovering Language History from Multilingual Resources
(2012) Avignon, France MDL-based models for alignment of etymological data (pdf)
Hannes Wettig, Suvi Hiltunen, Roman Yangarber. RANLP-2011: Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing
(2011) Hissar, Bulgaria MDL-based modeling of etymological sound change in the Uralic language family
Hannes Wettig, Suvi Hiltunen, Roman Yangarber. WITMSE-2011: The Fourth Workshop on Information Theoretic Methods in Science and Engineering
(2011) Helsinki, Finland Probabilistic models for alignment of etymological data (pdf)
Hannes Wettig, Roman Yangarber. Nodalida-2011: Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics
(2011) Riga, Latvia Hidden Markov models for induction of morphological structure of natural language
Hannes Wettig, Suvi Hiltunen, Roman Yangarber. WITMSE-2010: Workshop on Information Theoretic Methods in Science and Engineering
(2010) Tampere, Finland A Database of the Uralic language family for etymological research
Yangarber, R., Salmenkivi, M., Välisalo, M. University of Helsinki, Technical Report Series C; C-2008-38.
(2008) Helsinki, Finland